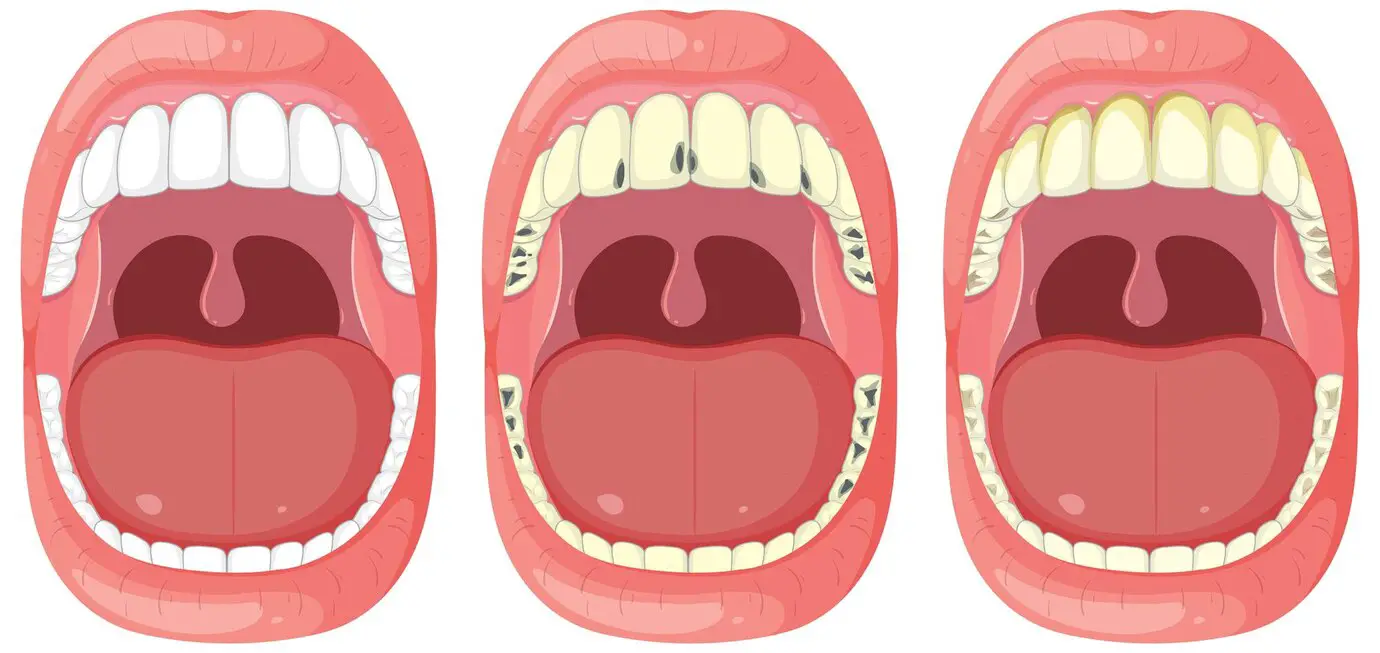
Tooth decay ranks among the most prevalent chronic conditions worldwide—affecting over 2.3 billion people globally, including nearly one in four adults in the United States. While cavities and enamel erosion have traditionally been managed with restorative procedures such as fillings and crowns, mounting research reveals that, in their earliest stages, tooth decay can be halted—and even reversed—through strategic dietary, oral-care, and lifestyle modifications. The key lies in supporting your body’s innate remineralization processes to restore enamel integrity before irreparable damage occurs.
In this in-depth, 2,000-word guide, we will:
-
Explain the science behind enamel demineralization and remineralization
-
Detail six natural, science-backed habits for preventing and reversing early decay
-
Provide a step-by-step recipe for a homemade toothpaste that whitens teeth, fights cavities, and promotes gum health
-
Offer professional tips on integrating these practices into your daily routine
By adopting these evidence-based strategies, you can empower your smile to heal itself, reduce reliance on invasive dental treatments, and maintain optimal oral health naturally.
1. The Science of Enamel Remineralization
Enamel, the hardest substance in the human body, protects underlying dentin and the tooth’s living pulp from bacterial invasion and mechanical wear. Composed primarily of hydroxyapatite crystals—a form of calcium phosphate—enamel is constantly challenged by acids produced when oral bacteria metabolize dietary sugars. This acidic assault initiates demineralization, leaching minerals from the enamel matrix. Fortunately, when the mouth’s pH rebounds and saliva delivers calcium, phosphate, and fluoride ions, remineralization can occur—rebuilding and strengthening the enamel.
Key factors influencing this dynamic balance include:
-
Salivary Flow and Composition: Saliva buffers acids and supplies essential minerals.
-
Dietary Mineral Intake: Adequate calcium, phosphate, magnesium, and vitamin D optimize the remineralization cascade.
-
Oral Hygiene Practices: Removing bacterial biofilm reduces acid production.
-
Exogenous Treatments: Fluoride and hydroxyapatite toothpastes accelerate crystal repair.
Understanding and leveraging these physiologic processes enables targeted interventions to reverse early carious lesions—white-spot decalcifications visible as chalky patches on enamel—before they progress to cavitation.
2. Tip 1: Eat for Strong, Remineralized Enamel
A balanced diet rich in enamel-fortifying nutrients provides the raw materials your teeth need to rebuild microscopic defects. Focus on:
2.1 Calcium: The Cornerstone Mineral
-
Mechanism: Calcium ions bind to demineralized enamel surfaces, forming new hydroxyapatite.
-
Best Sources: Dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt), fortified plant milks, almonds, broccoli, kale.
-
Professional Insight: A 2020 clinical trial demonstrated that daily consumption of high-calcium yogurt increased enamel microhardness by up to 15% over six months.
2.2 Vitamin D: The Absorption Enhancer
-
Mechanism: Regulates calcium and phosphate homeostasis, ensuring efficient intestinal uptake.
-
Best Sources: Sunlight exposure (10–20 minutes/day), fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), egg yolks, fortified cereals.
-
Clinical Note: Research published in the Journal of Dental Research linked optimal vitamin D levels (≥30 ng/mL) with a 40% lower risk of new caries in children aged 6–12.
2.3 Magnesium: The Synergist
-
Mechanism: Stabilizes hydroxyapatite crystals and modulates vitamin D activation.
-
Best Sources: Leafy greens (spinach, Swiss chard), nuts (cashews, almonds), seeds (pumpkin, flax), whole grains.
-
Dietary Tip: Pairing magnesium-rich foods with calcium sources (e.g., spinach salad topped with toasted almonds) enhances mineral synergy.
2.4 Phosphorus: The Structural Partner
-
Mechanism: Combines with calcium to reform the enamel’s mineral lattice.
-
Best Sources: Eggs, lean meats, poultry, fish, lentils, beans, nuts.
-
Evidence: A 2018 in vitro study found that topical phosphate applications promoted more uniform remineralized layer formation than calcium alone.
2.5 Foods to Limit
-
Sugary Snacks and Beverages: Sucrose, high-fructose corn syrup, and acidic drinks fuel cariogenic bacteria and erode enamel.
-
Sticky Carbohydrates: Candy, dried fruits, and starchy snacks adhere to tooth surfaces longer, prolonging acid exposure.
-
Acidic Foods: Citrus fruits, pickles, and carbonated beverages should be enjoyed in moderation and followed by rinsing with water.
By adopting an enamel-protective dietary pattern—often termed a “tooth-friendly” or “cariostatic” diet—you lay the foundation for sustained remineralization and cavity prevention.
3. Tip 2: Harness the Power of Oil Pulling
3.1 Traditional Origins, Modern Research
Oil pulling—an ancient Ayurvedic practice—entails swishing edible oil (most commonly coconut) through the mouth to eliminate bacteria and toxins. Contemporary studies reveal that oil pulling:
-
Reduces Colony-Forming Units of Streptococcus mutans, a primary caries-causing bacterium, by up to 70% after two weeks.
-
Decreases Plaque Index scores and gingival inflammation comparable to chlorhexidine mouthwash in randomized controlled trials.
3.2 How to Incorporate Oil Pulling
-
Choose a High-Quality, Organic Oil: Cold-pressed coconut oil (rich in lauric acid) offers antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory benefits.
-
Technique: Swish 1 tbsp of oil for 10–15 minutes, ensuring it reaches all quadrants.
-
Disposal: Spit into a trash receptacle—avoid drains to prevent clogging—and rinse thoroughly with water before brushing.
-
Frequency: Perform daily on an empty stomach, ideally first thing in the morning.
3.3 Safety and Precautions
-
Avoid Swallowing: Ingesting large amounts of oil may cause gastrointestinal upset.
-
Supplement, Don’t Replace: Continue using fluoride or remineralizing toothpaste; oil pulling is adjunctive, not a standalone therapy.
By incorporating oil pulling into your regimen, you can reduce microbial load, enhance saliva production, and create a more favorable environment for enamel repair.
4. Tip 3: Upgrade to a Natural, Enamel-Restoring Toothpaste
4.1 Why Switch from Conventional Formulations?
Many commercial toothpastes rely on harsh abrasives, synthetic detergents (e.g., sodium lauryl sulfate), and artificial sweeteners. While effective at cleaning, these ingredients can:
-
Strip natural oils from the oral mucosa
-
Create microabrasions in the enamel cuticle
-
Mask symptoms of underlying decay
4.2 Key Natural Actives for Remineralization
-
Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles
-
Function: Directly integrate into demineralized enamel rods, promoting crystal regrowth.
-
Evidence: A 2021 systematic review in Caries Research found hydroxyapatite toothpaste as effective as fluoride in reducing early-stage lesions.
-
-
Calcium Carbonate and Baking Soda
-
Function: Mildly abrasive to remove surface stains; neutralize plaque acids.
-
Safety: pH-neutral formulations protect against erosion.
-
-
Xylitol
-
Function: A nonfermentable sugar alcohol that starves S. mutans and boosts salivary flow.
-
-
Natural Fluoride Alternatives
-
For those avoiding fluoride, look for nanohydroxyapatite or bioactive glasses (e.g., calcium sodium phosphosilicate) to support enamel rebuilding.
-
4.3 Selecting the Right Toothpaste
When evaluating natural formulations, read labels for:
-
Ingredient Purity: Minimal additives, no artificial dyes or flavors.
-
Remineralizing Claims: Backed by clinical studies or ADA acceptance (in the U.S.).
-
Sensitivity Relief: Desensitizing agents like potassium nitrate can complement enamel repair.
By prioritizing toothpaste that actively replenishes lost minerals, you shift from merely cleaning to helping your enamel heal with every brush.
5. Tip 4: Reinforce with a DIY Mineral-Rich Mouthwash
5.1 Why a Mouthwash Matters
While toothbrushing addresses dental surfaces, a targeted mouth rinse reaches interdental spaces and the entire oral cavity—delivering buffering agents and minerals directly to enamel and the gums.
5.2 Simple Mineral Mouthwash Recipe
Ingredients
-
½ tsp fine sea salt (natural source of trace minerals)
-
½ tsp baking soda (sodium bicarbonate to neutralize acids)
-
1 cup lukewarm filtered water
-
(Optional) 2 drops therapeutic-grade clove or peppermint essential oil for antimicrobial action and fresh breath
Instructions
-
Dissolve salt and baking soda in the warm water.
-
Add essential oil, stirring gently.
-
Swish 30–60 seconds, then spit.
-
Rinse with plain water if desired; do not ingest.
5.3 Benefits and Evidence
-
pH Stabilization: Baking soda raises oral pH, reducing acid-mediated demineralization.
-
Antimicrobial Effects: Sea salt and clove oil demonstrate in vitro inhibition of cariogenic bacteria.
-
Scalp Analogy: Just as a mineral rinse can soothe a dry scalp, this formula nurtures enamel and gingival health without harsh chemicals.
Use this mouthwash once or twice daily—after brushing and flossing—to fortify your tooth’s natural defenses.
6. Tip 5: Leverage Herbal Allies for Oral Health
6.1 Clove Oil: The Time-Tested Analgesic
-
Active Compound: Eugenol, a phenolic compound with potent antibacterial and analgesic properties.
-
Usage: Dilute 1 drop in a teaspoon of carrier oil (coconut or olive). Apply directly to inflamed gums or tender spots using a cotton swab.
-
Caution: Avoid undiluted clove oil, which can irritate mucous membranes.
6.2 Neem: India’s Oral-Health Superhero
-
Mechanism: Contains nimbidin and azadirachtin, which inhibit plaque formation and bacterial adhesion.
-
Form: Neem twig brushes, neem leaf extracts, or neem-infused toothpaste.
-
Evidence: A randomized trial in Pharmacognosy Research reported neem mouthwash reduced gingivitis scores by 45% over 21 days—comparable to chlorhexidine.
6.3 Licorice Root: The Anti-Plaque Powerhouse
-
Active Compounds: Glycyrrhizin and glabridin, which suppress S. mutans and prevent biofilm formation.
-
Usage: Chew on a clean piece of licorice root or use licorice extract mouthwash.
-
Benefit: Adds a naturally sweet flavor without cavity-promoting sugars.
By integrating herbal remedies—clove for pain relief, neem and licorice for plaque control—you harness millennia-old traditions validated by modern research.
7. Tip 6: Stay Hydrated to Boost Saliva’s Protective Role
7.1 Saliva: Your Mouth’s Natural Defense
Saliva performs critical functions:
-
Buffering Acids: Neutralizes plaque acids within seconds of pH drop.
-
Mineral Delivery: Supplies calcium and phosphate for remineralization.
-
Antimicrobial Action: Contains lysozyme, lactoferrin, and immunoglobulins that suppress pathogens.
7.2 Hydration and Lifestyle Habits
-
Daily Water Intake: Aim for at least 8 cups (1.9 L) of water, adjusted for body weight, activity level, and climate.
-
Stimulate Saliva: Sugar-free chewing gum (xylitol-sweetened) and lozenges encourage flow.
-
Avoid Xerostomia Triggers: Alcohol, caffeine, tobacco, and certain medications (antihistamines, antidepressants) can reduce saliva production.
Maintaining optimal hydration and saliva production is a cornerstone of both preventing new decay and promoting enamel repair.
8. DIY Enamel-Restoring Toothpaste: A Professional Recipe
Beyond commercial formulations, you can craft your own potent toothpaste that whitens, fights cavities, and soothes your gums—all with natural, readily available ingredients.
8.1 Why Homemade Toothpaste?
-
Ingredient Control: Eliminate unnecessary fillers, synthetic flavors, and harsh detergents.
-
Targeted Benefits: Customize the formula for remineralization, sensitivity relief, or gum care.
-
Cost-Effective: Baking soda, coconut oil, and clay are affordable pantry staples.
8.2 Ingredients and Their Roles
| Ingredient | Function |
|---|---|
| 3 Tbsp Baking Soda | Mild abrasive; neutralizes acids; combats bacteria |
| 3 Tbsp Extra-Virgin Coconut Oil | Rich in lauric acid; antimicrobial; anti-inflammatory |
| 3 Tbsp White Kaolin Clay | Gently polishes; balances pH; adsorbs toxins |
| 15 drops Mint or Lemon Essential Oil | Provides flavor; antibacterial; freshens breath |
8.3 Preparation Method
-
Measure and Combine: In a nonreactive bowl, blend baking soda and clay until homogeneous.
-
Incorporate Oils: Gently warm coconut oil if solid; stir into the dry mixture.
-
Flavor and Preserve: Add essential oil drops; mix thoroughly.
-
Adjust Consistency: For a thicker paste, add more clay; for creamier texture, increase coconut oil slightly.
-
Storage: Transfer to a sanitized glass jar with a tight lid. Keep at room temperature; coconut oil may solidify below 76 °F/24 °C—use a small spatula to apply.
8.4 Usage Guidelines
-
Apply Sparingly: A pea-sized amount on your toothbrush is sufficient.
-
Brush Gently: Use a soft-bristled brush in gentle circular motions for two minutes.
-
Frequency: Brush twice daily—morning and evening—followed by flossing and a quick rinse with your mineral mouthwash.
-
Monitor Reactions: Discontinue use if you experience persistent irritation or allergic response to essential oils.
9. Integrating These Habits into Your Daily Routine
Changing oral-care habits takes commitment. Here’s how to incorporate these six strategies seamlessly:
-
Morning Routine
-
Brush with your homemade or natural remineralizing toothpaste.
-
Rinse with DIY mineral mouthwash.
-
Chew xylitol gum after breakfast to neutralize any residual acids.
-
-
Midday Practices
-
Snack on cheese or raw almonds to supply calcium.
-
Sip water throughout the day; avoid sugary beverages.
-
If feasible, perform a quick 5-minute oil pulling session before lunch.
-
-
Evening Protocol
-
Eat a nutrient-dense dinner emphasizing leafy greens, lean protein, and dairy or fortified alternatives.
-
Oil pulling upon waking or before bedtime—whichever suits your schedule.
-
Brush and floss with gentle, circular strokes; follow with herbal-infused clove oil application for tender gums.
-
Finish with a lukewarm rinse of mineral mouthwash.
-
-
Weekly Check-Ins
-
Prepare a fresh batch of homemade toothpaste.
-
Perform a self-assessment of gum health—bleeding, swelling, or pain warrant professional evaluation.
-
Replace toothbrush head every 3 months or after illness.
-
10. When to Seek Professional Care
While early-stage decay often responds well to these natural interventions, certain signs indicate the need for professional dental evaluation:
-
Persistent White-Spot Lesions that do not improve after 4–6 weeks of remineralizing care
-
Tooth Sensitivity to cold, heat, or sweets that disrupts daily activities
-
Visible Cavities or Pits in enamel
-
Gum Bleeding or Recession despite improved home hygiene
-
Chronic Bad Breath or Taste Alterations
A licensed dentist can assess lesion severity via visual inspection, digital radiographs, and transillumination. When necessary, minimally invasive treatments—such as resin infiltration (ICON) or glass ionomer sealants—can arrest decay progression while preserving natural tooth structure.
Conclusion
Early tooth decay need not spell a lifetime of fillings and invasive restorations. By embracing a holistic approach—combining a mineral-rich diet, targeted oral-care rituals, natural and DIY products, and professional guidance—you empower your smile to heal and remain resilient. Remember:
-
Enamel Strength Requires Minerals: Prioritize calcium, vitamin D, magnesium, and phosphorus.
-
Harness Natural Antimicrobials: Oil pulling, clove oil, neem, and licorice root support a balanced oral microbiome.
-
Use Remineralizing Agents: Hydroxyapatite, baking soda, and clay in toothpaste and mouthwash rebuild enamel on a microscopic level.
-
Optimize Saliva Flow: Hydration, xylitol gum, and stress reduction keep your natural defenses strong.
With consistency, you can reverse early enamel lesions, fortify your teeth against future challenges, and maintain a radiant, healthy smile—naturally. Whether you adopt our six proven tips, experiment with the homemade toothpaste recipe, or consult your dentist for personalized care, each choice you make today builds stronger, cavity-resistant teeth for tomorrow.